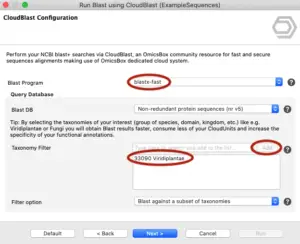
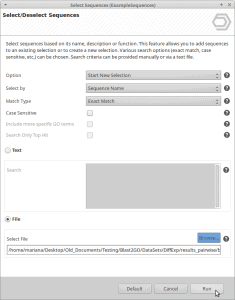
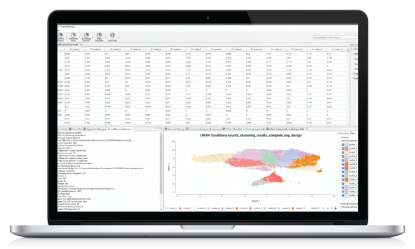
IsoSeq De-Novo Isoform Discovery with OmicsBox
Introduction The IsoSeq sequencing method produces full-length transcripts using Single Molecule, Real-Time (SMRT) Sequencing. Long read lengths allow sequencing of full-length transcripts up to 10 kb or longer, removing the need for transcript assembly or inferencing. Therefore, unlike traditional short-read methods, IsoSeq provides a more accurate and complete view of gene expression and alternative splicing events. This comprehensive understanding of